Explain How Homologous Chromosomes Are Different From Sister Chromatids
Homologous chromosomes are basically two similar chromosomes inherited from father and mother. A chromosome occurs throughout the cells life cycle.

Meiosis I Biology For Non Majors I
Pairs of chromatids separated in 2nd division.
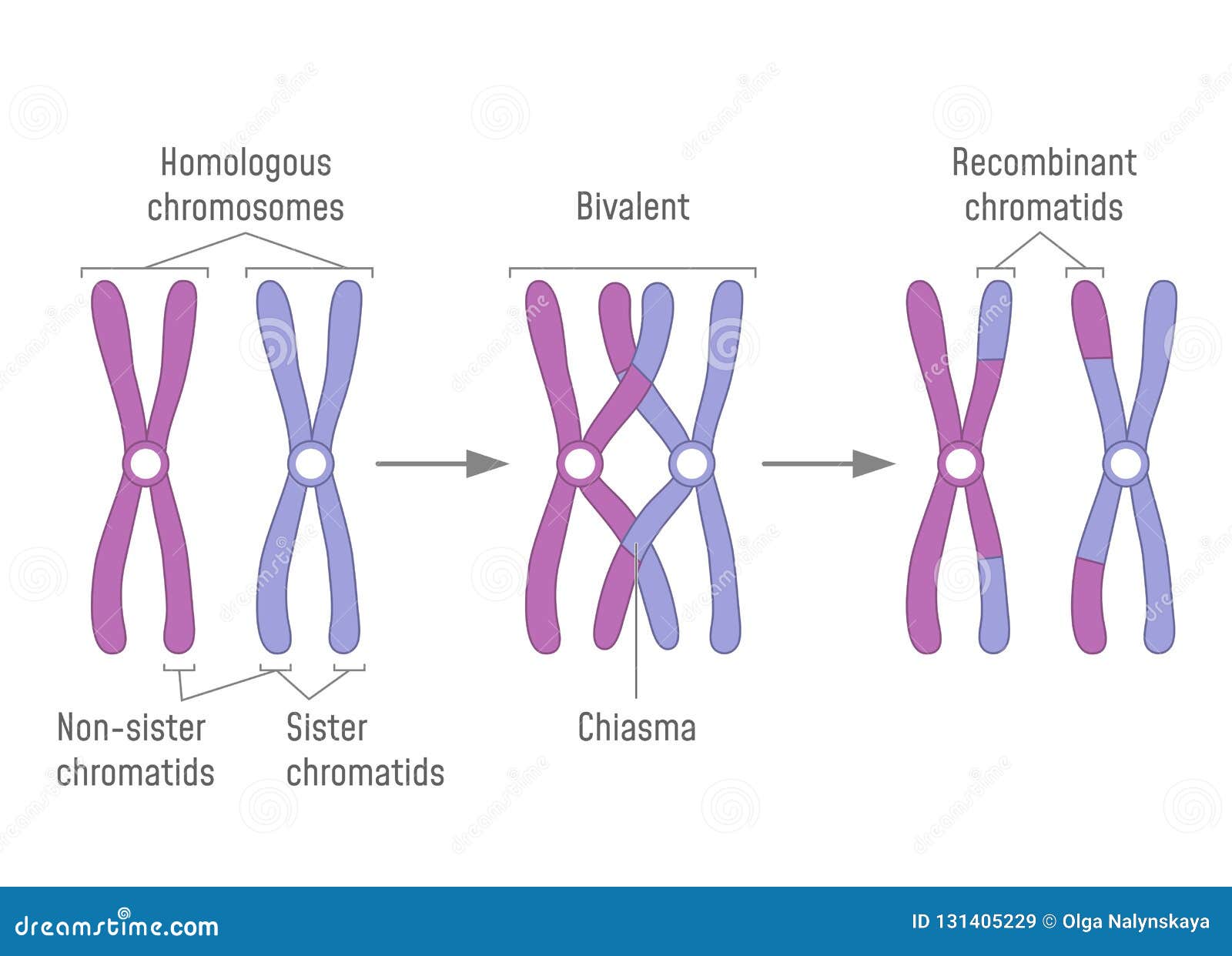
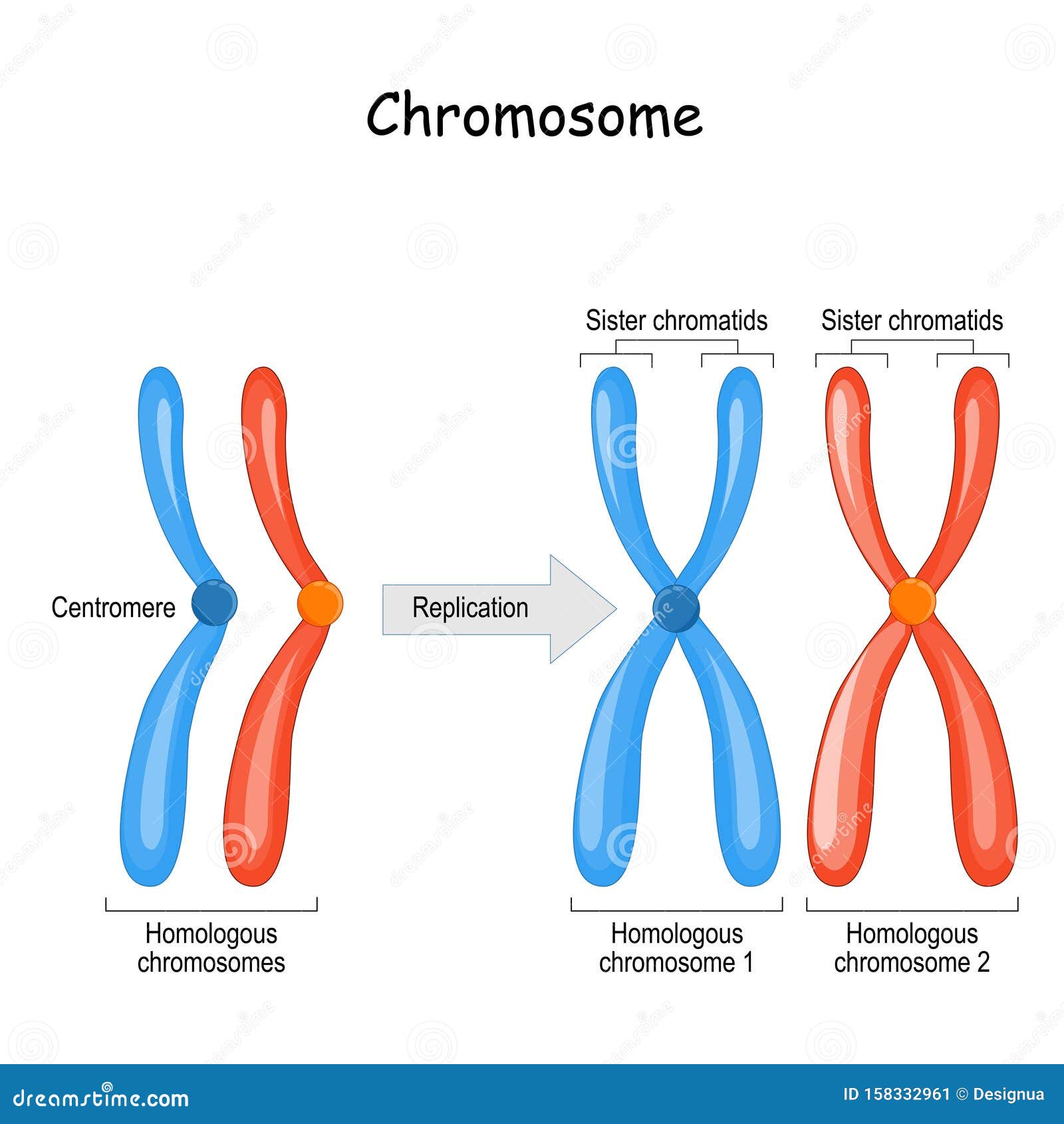
. Chromosomes condense and they associate in homologous pairs. Humans have 23 different chromosomes n 23 for a diploid number of 46 2n 46. Sister chromatids are multiple versions of the same chromosome that are interconnected together throughout the centromere.
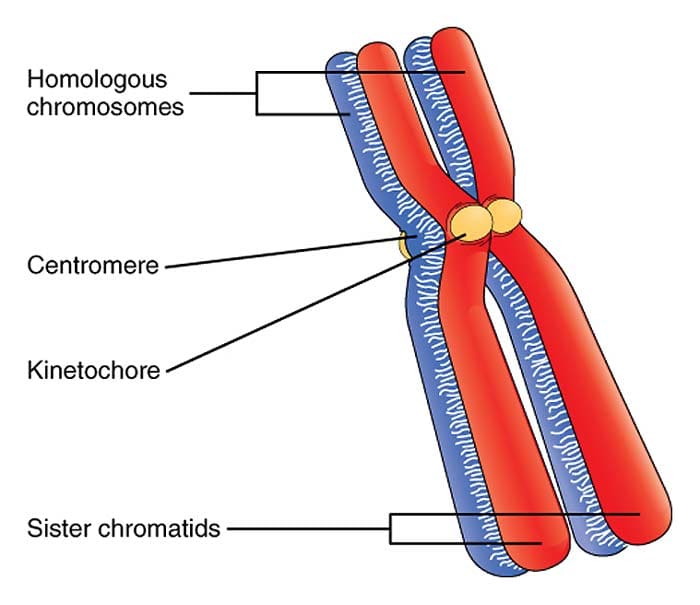
During metaphase each of the 46 chromosomes line up along the center of the cell at the metaphase plate. Homologous chromosomes are paired up after fertilisation so one is from you mum and one is from your dad therefore even though they carry the same genes thats why they pair up they have different variations of them - alleles. Sister chromatids held together by centromere.
Chromosomes is rolled up DNA when it is going through cell division. Hence the two are identical or exactly similar. Homologous chromosomes contain the same gene loci but may have different alleles of a particular gene.
During which phase of mitosis do the sister chromatids move apart. Each of the chromosomes that make up the homologous pair is derived. They have the same genes but not necessarily the same alleles so they could carry hair color one with brown the other with blonde.
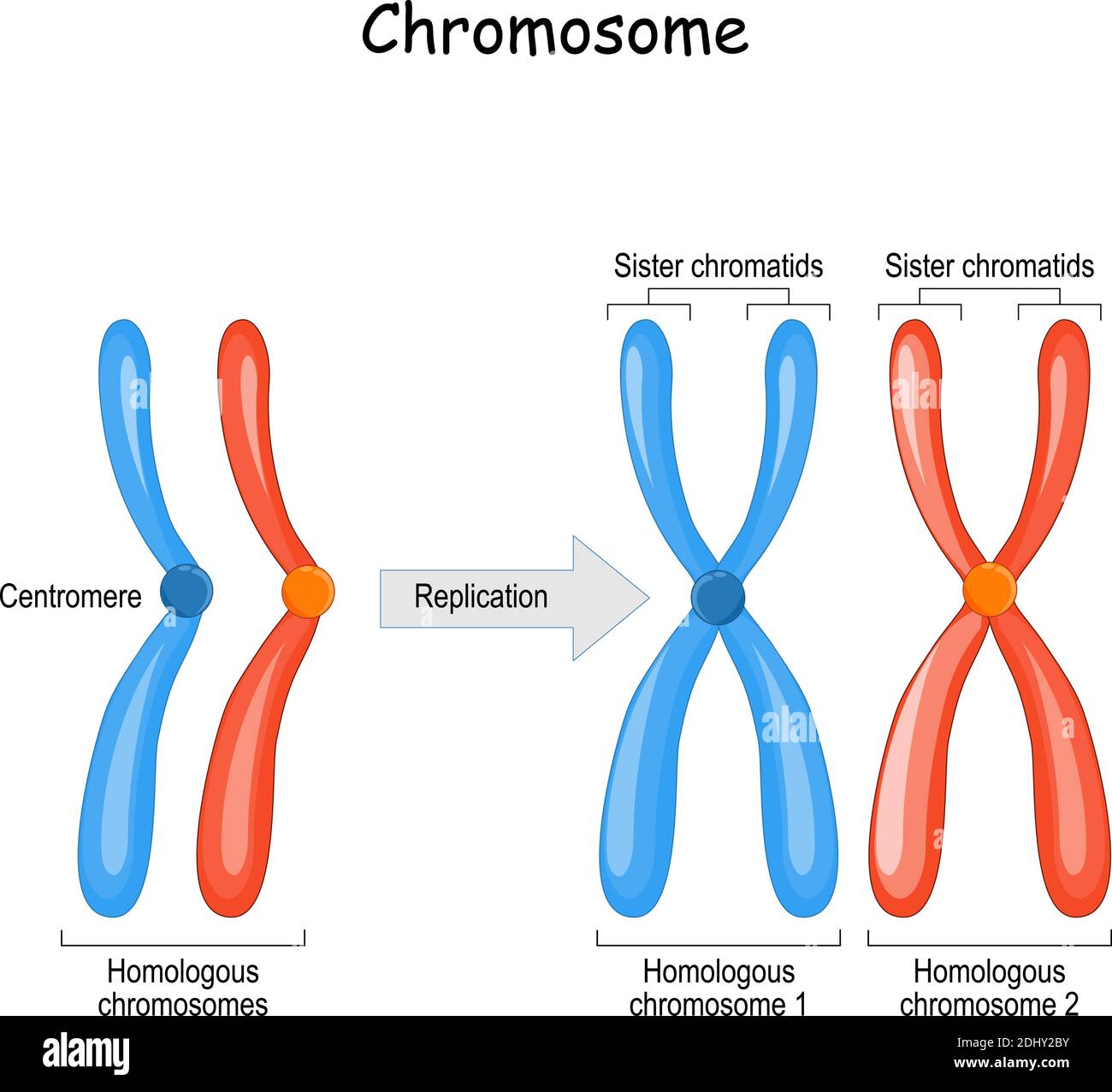
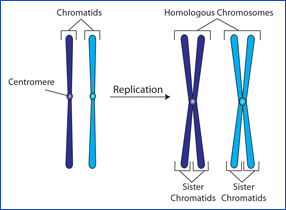
Humans for example have 46 chromosomes 23 pairs. Sister chromatids are identical copies of each other produced during DNA replication. Ater DNA replication two sister chromatids in a single chromosome are held together at their centromeres by.
Genes on sister chromatids are identicalhomologousunrelated Homologous genes are identicalsimilarunrelated Crossing over that recombines genetic information occurs between homologous chromosomessister chromatids. How many chromatids are there in 4-6 chromosomes. Sister chromatids are essentially a replicate or a copy of the original chromatid.
During mitosis DNA condenses to form visible chromosomes and these two identical copies or sister chromatids are attached to each other and form an X shape. The spindle fibers will move the chromosomes until they are lined up at the spindle equator. During anaphase the centromere splits allowing the sister.
Chromosomes are not exact copies of each other. Chromosomes still double structures. Chromatin is a long chain of DNA.
Chromosomes are moving apart. Homologous chromosomes carry different alleles. Therefore each chromosome is made up of 2 sister chromatids for a total of 92 chromatids.
As for homologous chromosomes basically thats where sexual reproduction comes in. If you were to condense them at this unreplicated stage they would be known as chromosomes as well but when they replicate both sides are known as sister chromatids and the whole structure is known as a chromosome. They are homologous because they have the same genes though not same alleles.
These are a combination of one maternal and one paternal genotype that are partnered together during fertilization in a gamete. Homologous chromosomes are of the same shape and size they may or may not contain the same genes and they are certainly not a duplicate version of one another. Sister Chromatids are identical copies of each other.
A sister chromatid is the duplicate of each of the pair of homologous chromosomes. Thats a very interesting question. Sister chromatids held together by centromere.
Sister chromatids are the branches of the same chromosome. While sister chromatids are exact copies of each other non-sister chromatids come from homologous chromosomes. Although both are very similar the difference between the two is the pairing.
Homologous chromosomes are two sister chromatids stuck together with cohesions forming a tetrad. Chromosomes in homologous pair. Answer 1 of 2.
Homologous chromosomes are similar in size and shape they have the same genes and originate from different parents sister chromatids are found in replicated chromosomes and contain exact copies of the single double-helical molecule of DNA. Therefore each chromosome is made up of 2 sister chromatids for a total of 92 chromatids. Parameters of Comparison.
During meiosis the homologous chromosomes pair up during first prophase. Homologous chromosomes are closely associated with each other in both mitosis and meiosis. You might find it helpful to think about sisters chromatids as twin siblings and homologous chromosomes as parents.
Sister chromatids are only associated with each other during mitosis. Because DNA replication has occurred. The correct answer is B.
Describe how crossing over occurs during meiosis 1- 2. These join to spindle fibres form and the chromosomes line up in the centre Homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles where they separate. Describe what has happened during division 1 in the figure above.
See in a normal cell after inter phase the chromosome number is 46 and the number of chromatid is 92 which means 2 chromatids 1 chromosome after mitosis they become 46 chromosome in each daughter cell but have 46 chromatids in each daughter. Homologous chromosomes contain the same gene loci but may have different alleles of a particular gene. Anaphase 1- description meiosis anaphase I.
A diploid cell has 1234 set s of homologous chromosomes. So homologous chromosomes share the same geneHomologous chromosomes are similar but not identical. Homologous chromosomes are the two chromosomes that make a chromosome pair.
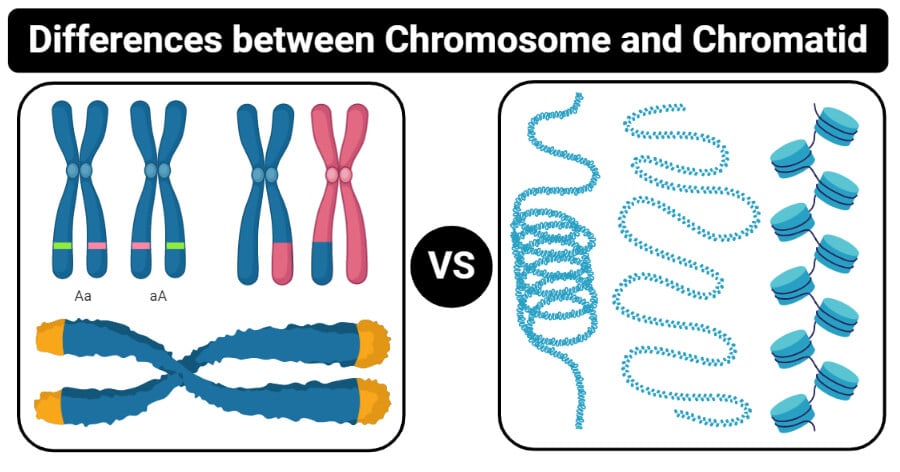
Chromatin is the shape a very long and continuous chain of DNA chromosomes take on before mitosis or meiosis. A chromatid on the other hand are created only when the cell pass through mitosis or meiosis stages. Chromosome is formed of two chromatids.
They code for the same genes but are not genetically identical. Difference Between Homologous Chromosomes and Sister Chromatids Homologous chromosomes contain two similar chromosomes and each chromosome in the pair contains two sister chromatids. Chromatin only begins to form into chromosomes in the beginning of mitosis or.
One copy of gene comes from each parent. A haploid cell has 1234 allele s for each gene in its genome. One homologous chromosome comes from the father and the other comes from the mother.

Sister Chromatids And Non Sister Chromatids What Is The Difference Now I Know

Meiosis Pg 45 46 Sc 912 L Describe The Process Of Meiosis Including Independent Assortment And Crossing Over Explain How Reduction Division Ppt Download
Difference Between Homologous Chromosomes And Sister Chromatids Difference Between

Sister Chromatids Stock Illustrations 31 Sister Chromatids Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
Homologous Chromosomes High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
How Do Sister Chromatids Differ From Homologous Chromosomes How Do These Differences Affect Their Functions Quora
What Is A Homologous Chromosome Biology Explorer
What Is The Difference Between Homologous Chromosomes A Pair Of Homologous Chromosomes And Also Chromatids Quora

Solved How Are Sister Chromatids And Homologous Chromosomes Different From Each Other Homologous Chromosomes Are Identical Copies Of Each Other One Sister Chromatid Comes From The Father And One Comes From The Mother

Solved What Is The Difference Between Homologous Chromosomes Chegg Com
Difference Between Homologous Chromosomes And Sister Chromatids Difference Between

Solved Explain The Relationship Between Homologous Chegg Com
Topic 10 1 Meiosis Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green
How Do Sister Chromatids Differ From Homologous Chromosomes How Do These Differences Affect Their Functions Quora
Difference Between Homologous Chromosomes And Sister Chromatids Pediaa Com

Sister Chromatids And Homologous Chromosomes Youtube
Difference Between Homologous Chromosomes And Sister Chromatids Difference Between
Sister Chromatids Stock Illustrations 31 Sister Chromatids Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
Comments
Post a Comment